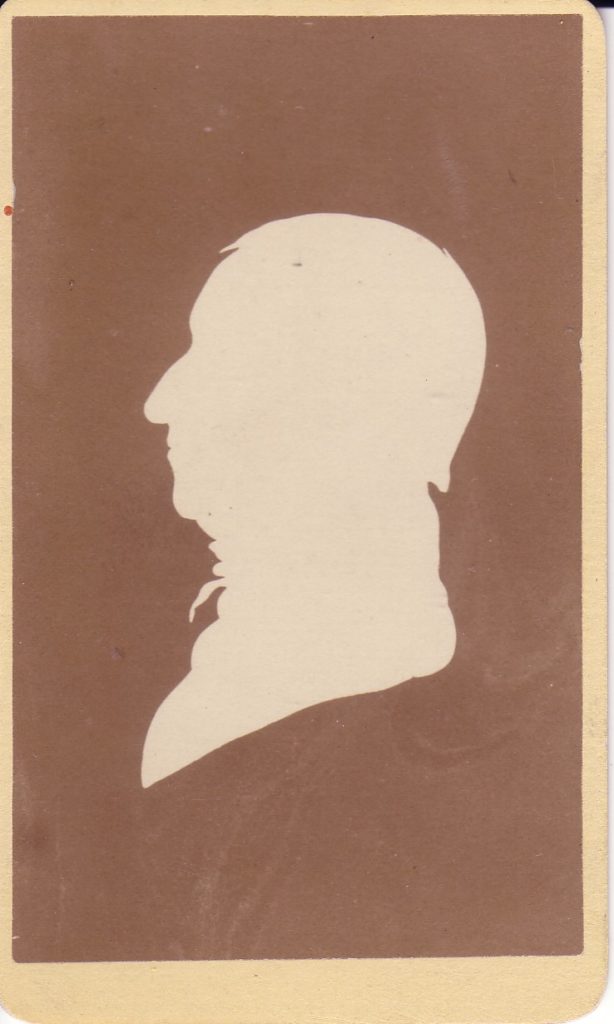
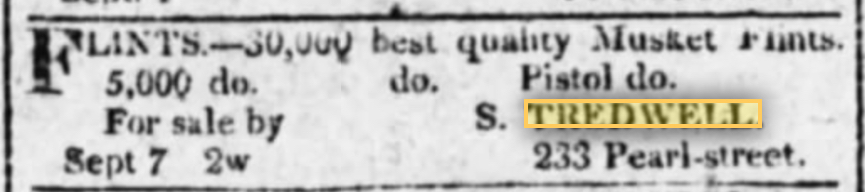Meet the Tredwells: Seabury Tredwell, Part 4 – The End of an Era
by Ann Haddad
..
On February 4, 1835, a notice appeared in the Shipping and Commercial List and New-York Price Current that the hardware firm of Tredwell, Kissam, and Company, which had flourished for over 20 years on Pearl Street, was “dissolved by mutual consent.”
That same year, Seabury Tredwell moved his family from their home on Dey Street, in lower Manhattan not far from the seaport, to a Late Federal/Greek Revival row house on Fourth Street, in the neighborhood then known as the elite “Bond Street area.” He was 55 years old, and not about to retire from the world. For 30 years until his death he maintained an active life, keeping pace with the enormous economic changes taking place in New York City and making shrewd investments in real estate, railroads, and natural gas. (For more information about Seabury Tredwell’s hardware business and investments, see Seabury Tredwell: The Merchant Years and Seabury Tredwell: Man of Opportunity). His years of hard work led to outstanding success and enormous wealth. Now we turn our attention to his final illness and death in March 1865.
..
..
..
Seabury’s Final Illness
For some years leading up to his death, Seabury’s attending physician was Dr. George E. Belcher (1818-1890), a practitioner of homeopathy, an alternative medical practice. Dr. Belcher had converted to homeopathy from conventional medical treatments in 1844. (For more information about homeopathy and the Tredwell family’s physicians, see my blog post of October 2016: The Doctor in the House is a Homeopath!). Seabury’s death certificate, signed by Dr. Belcher, states he died from acute kidney failure caused by Bright’s Disease, now known as acute or chronic nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys). The disease is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including swelling, coma, stroke, convulsions, and blindness.
Seabury’s homeopathic treatment plan likely included the administration of herb and plant remedies, such as arsenicum, belladonna, burdock root, and juniper berry; dietary restrictions (no red meat, cheese, or alcohol); warm compresses and massage of the lower back for pain; and inhalation of lavender oil to reduce anxiety.
Although Dr. Belcher listed Bright’s Disease as the cause of death on Seabury’s death certificate, we do not know how long he suffered with the disease. According to a story related by his granddaughter Elizabeth Tredwell Stebbins (1885-1973), Seabury caught a cold after returning from his home in Rumson, New Jersey, by boat one winter’s day in 1865, which led to his death on March 7. On March 3, his nephew Timothy Tredwell, who lived in Toledo, Ohio, penned a letter to Seabury’s daughter Julia, after learning of his condition:
“I am deeply pained by the news of your dear father’s illness & his sufferings occupy much of my daily & nightly thoughts & sympathies… May god in his infinite mercy bless him. He has been a good uncle to me & how good a father to you all, you only can tell.”
The Civil War Draws to a Close
In early 1865, as Seabury’s life was coming to an end, the nation witnessed the collapse and death of the Confederacy. The Union Army, thanks to the brilliant military strategies of Generals Ulysses S. Grant and William T. Sherman, left the Confederate Army in tatters. Passage of the 13th Amendment at the end of January 1865 abolished slavery and on March 4, Abraham Lincoln was inaugurated as President for a second term in Washington, D.C. One month later, on April 9, the Civil War ended when General Robert E. Lee surrendered to General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House, Virginia.
The Union Jubilee
On March 6, as Seabury lay on his deathbed, surrounded by his family, New York City joyously celebrated the anticipated end of the Civil War with a “Union Jubilee.” Over one million spectators lined the streets to see the grand parade, which included military troops; volunteer firemen; members of clubs, businesses, and community organizations; and even a menagerie of, among other animals, elephants and camels. John Ward, Jr., who was a National Guardsman and who lived near the Tredwells, on Thompson and Bleecker Streets, marched in the parade with his Company; the excitement of the event is palpable in his diary entry:
“Beautiful, perfect day. I put on my uniform and medal after breakfast & rigged the flag out of Mother’s window. …We formed in Washington Square….Tremendous crowd. Largest ever known. We wheeled well into Broadway, marched down to the Museum, up Park Row, etc., and Bowery to Union Square (where we saw the procession still passing down Broadway) up 4th Avenue, to 23rd Street, up Madison Ave. to 29th St…up to 33rd St. over to 8th Ave., down to Washington Square where we were dismissed. Flags & decorations were fine. …Dined. Then went to Union Square to see the fireworks. Great crowd. Splendid pieces. Change of rebel to loyal flag. “Sumter” “Bombardment of Fort Fisher,” “Monitor & Merrimack” etc. Rockets & balloons. Homes and clubs illuminated. Mother had gas all lighted.”
As the Tredwell family maintained their vigil at Seabury’s deathbed that day, they surely heard the commotion of the celebration, the pealing church bells, and the gun salute fired in Union Square to signal the start of the parade. It is hard to imagine them sharing in the immense relief and happiness of the citizens of New York City. And the no doubt unadorned Tredwell home on Fourth Street must have stood out sharply among its neighboring dwellings, for The New York Daily Herald reported on March 7:
“Looking at the houses, you beheld one, grand continuous exhibition of flags from windows, poles, awnings, and every point whereon to hang this badge of loyalty and nationality. All of the hotels and public buildings were covered with the Stars and Stripes, and many houses displayed mottoes and inscriptions of an appropriate character.”
 |
Death of the Patriarch
The day after the “Union Jubilee,” on March 7, Seabury died at the age of 84. His wife, Eliza, their eight children, and five grandchildren, survived him. After being waked in the front parlor for three days, on March 11 (a “beautiful, bright cold day,” according to John Ward, Jr.), Seabury’s funeral took place in the double parlor of his home, and he was interred in the New York City Marble Cemetery on East Second Street. On December 28, he was moved to his final resting place in the family plot in Christ Church Cemetery in Manhasset, Long Island.
A Family, and a Nation, Mourn
Eliza Tredwell and her family were approximately one month into their mourning period for Seabury when the American Civil War ended on April 9, 1865. Five days later, on April 14, President Lincoln was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth, and the glory of the Union victory was instantly forgotten, as the City plunged into mourning. Philip Hamilton Hill (1839-1915), a 27-year-old York City dry-goods clerk, noted the tragedy in his diary on April 15:
“Was horrified on waking this morning, to hear that President Lincoln was assassinated last night at Ford’s Theatre, Washington, by a man supposed to be J. Wilkes Booth the actor, and that an attempt had been made, upon the life of Sec’y Seward. Business was at a standstill all day, many of the Stores being closed, and most all draped in mourning, and a feeling of intense excitement existed throughout the City.”
On Tuesday, April 25, Hill recorded in his diary how he joined the crowd (over 150,000 mourners) which lined up outside City Hall, from which hung a banner reading “THE NATION MOURNS,” to view the late President’s body, and the somber mood as Lincoln’s funeral cortege passed through New York City:
“By dint of hard work, and a good deal of tight squeezing, I managed to get through. I wouldn’t go through the same crowd again for ten dollars…The remains lay at the door of the Governor’s room, surrounded by a guard of honor…He looked the same as in life, with the exception of his skin, which was of a much darker hue….At 1 P.M. all the stores were closed, and the funeral procession commenced to move up Broadway towards the train on the Hudson River road which was to convey the remains West. Had our room full of company to view the procession.”
One wonders if any of the Tredwell family joined Hill at City Hall to view the President’s remains. They most likely joined the half a million New Yorkers who viewed the funeral procession, as it made its way up Broadway past Fourth Street. Even in their mourning attire, they would not have stood out in the crowds, for on that day many women donned widow’s weeds, and the men wore black crepe armbands, as a sign of their grief over President Lincoln’s death.
A Long Mourning Period
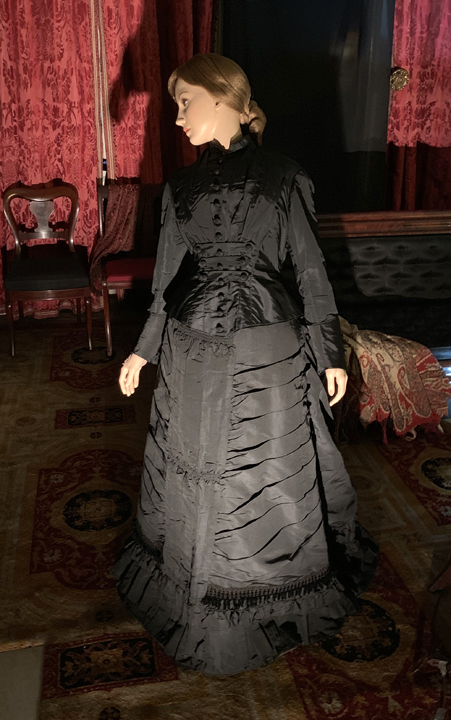
Mourning, the personal expression of loss and grief, was considered women’s work in the 19th century. Men, as the breadwinners who had to return to the workforce, were not expected to remain at home and follow the societal restrictions required by mourning etiquette. They donned a black hatband or armband and resumed their regular life. It fell to the women of the house to conform to social norms, by donning black mourning attire, sharply curtailing their socialization, and following the other precise rules of mourning frequently found in popular household manuals. The ability to follow elaborate mourning rituals was also a subtle indication of the wealth, respectability, and social status of the family; mourning attire and its accoutrements were expensive.
For Eliza Tredwell, mourning and all its associated traditions became a daily part of her life, perhaps for the remainder of her life. Typically, a widow in “full” or “deep” mourning adhered to a strict dress code of dull black for a year and one day, then proceeded, in the ensuing nine months to one year, to “half-mourning,” in which some colors, such as gray, white, mauve, and lavender, were permitted.
For much more information about mid-19th century mourning customs, please visit our exhibition “Death, Mourning, and the Hereafter in Mid-19th Century New York,” on view from September 26 to November 4. As part of the exhibition, visitors may meet Mrs. Tredwell in the front parlor and offer their condolences every Saturday afternoon in October from 1:30-3:30 p.m.
The End of an Era
An obituary in the New York Post on March 11, 1865, noted Seabury’s death:
“Among the deaths noticed in our column today is that of one of our oldest and most respected merchants, Seabury Tredwell. He was a gentleman of the old school, dignified and accomplished in his manners and high-minded and honorable in all his transactions…“He now goes out from us, one of the last of his generation, honored, respected and beloved by all.”
Sources:
- Hill, Philip Hamilton. Diaries, 1855-1865. Manuscripts Division, New-York Historical Society.
- Knapp, Mary L. An Old Merchant’s House: Life at Home in New York City, 1835-65. New York: Girandole Books, 2012.
- New York Daily Herald. March 7, 1865, p. 1. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 9/17/19.
- New York Evening Post. March 11, 1865. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 9/9/19.
- New York, New York City Municipal Deaths, 1759-1949. www.familysearch.org.
- Merchant’s House Museum Archives. Tredwell, Timothy. Manuscript Letter, March 3, 1865. MHM 2002.4601.32.
- Shipping and Commercial List and New-York Price Current. February 4, 1835, p. 3. America’s Historical Newspapers, via ProQuest. Accessed 6/29/17.
- Spann, Edward K. Gotham at War: New York City, 1860-1865. Wilmington, DE: Scholarly Resources, Inc., 2002.
- Strausbaugh, John. City of Sedition: The History of New York City During the Civil War. New York: Twelve Hachette Book Group, 2016.
- Ward, John. Diaries, 1847-1888. Manuscripts Division, New-York Historical Society.
Meet the Tredwells: Seabury Tredwell, Part 3 – Man of Opportunity
by Ann Haddad
An Astute Businessman
George Chapman, who founded the Merchant’s House Museum in 1936, named it “The Old Merchant’s House” as a tribute to the early 19th century merchants who were known as the old merchants, among them Seabury Tredwell, who built New York City into the “commercial emporium of America” (as was said in the 19th century). However, Seabury Tredwell’s occupation certainly did not define him. Although he was a New York City hardware merchant (and a very successful one: see my post Seabury Tredwell, Part 2 – The Merchant Years), he did not confine his business interests to his Pearl Street warehouse and to life on the seaport. Rather, Seabury held a progressive view of the city and the nation’s capacity for growth; beginning in 1816, he began to invest in real estate, an interest that would continue until his death. As his career flourished, he purchased properties in Manhattan and Brooklyn, as well as further afield in North Carolina and Michigan. Seabury also kept abreast of the country’s industrial development, investing in the burgeoning railroad and coal gas companies.
New York on a Grid
Relatively early in his career (and just one year after taking on his nephew as a business partner), Seabury Tredwell started investing in the New York City real estate market. No doubt he was influenced and guided by two of his older brothers, Adam and John, who had moved to the city several years before Seabury, and who, by the first decade of the 19th century, owned extensive real estate in New York City and Brooklyn City. Seabury’s real estate investing involved him in one of the most important chapters of New York City history: the Commissioners’ Plan of 1811, which called for the reorganization of Manhattan’s haphazard landscape into streets and avenues in a rectilinear grid pattern. Seabury’s first real estate purchase indicates that he was very likely aware of the Commissioners’ Plan. Probably eager to profit from the city’s anticipated growth patterns, in May 1816, prior to his marriage and while living in a boarding house, Seabury purchased a substantial three-lot parcel on the northwest corner of what is now 12th Street and Broadway, for $1,860.
The City Pays
In 1826, ten years after Seabury purchased the property, New York City was preparing to open 12th Street; the first step of the process was to compensate all the property owners whose land would be claimed and used. According to the Minutes of the Common Council, on January 28, 1828, the city paid Seabury $3,341 for one lot of his property that was consumed by the grid. Nine other property owners also received payment.
Harlem Land
In December 1828, Seabury sold one of the remaining lots on 12th Street and Broadway to Michael Floy for $800, in exchange for 4 lots on 128th Street and 4th Avenue, in Central Harlem. Floy, a noted horticulturist, likely wanted the land to add to his already existing greenhouse south of what is now Union Square. The land in Harlem was a developing area, ideal for real estate speculation. Further research is required to determine if and how Seabury built on and profited from the Harlem investment.
A Wise Investment
Seabury sold the last lot on the property on 12th Street in February 1833 for $1,500. Seabury gained usable land in Harlem and realized a total profit of $5,641 from his original investment of $1,860.
The New York Merchant’s Exchange
In addition to his personal real estate dealings, Seabury bid at auction for some of his properties at the New York Merchant’s Exchange, located at 55 Wall Street. Built in 1836-42, it replaced the original Exchange, which was destroyed in the Great Fire of 1835. The Exchange housed a post office, banks, and the Chamber of Commerce, as well as rooms for auction sales of real estate and stocks, which was at a fever pitch as the city growth pushed northward, and housing was in great demand to accommodate the exploding population.
According to the records of New York Merchant’s Exchange of July 17, 1856, Seabury purchased at auction a lot on the southwest corner of 8th Avenue and 53rd Street, for $4,050.
Seabury Bets on Brooklyn
When Seabury ventured into the frenzied Brooklyn real estate market in the mid-19th century, Brooklyn was the third largest city in America (it didn’t merge with New York City until 1898), and soon to become one of America’s major industrial centers, due to its location on the East River, which allowed for convenient transportation of materials and manufactured goods. Beginning in 1814, regular steam ferry service between Fulton Street in Brooklyn and Beekman Slip (now Fulton Street) in Manhattan, made it easy for affluent families who had moved to Brooklyn, as well as workers with jobs in the city, to commute back and forth.
.
.
Before It Was DUMBO
Seabury no doubt was aware of Brooklyn’s changing character and landscape when he acquired his first piece of Brooklyn property in March 1852, when he purchased, from the estate of his brother John, four plots on Fulton and Pearl Streets in the Second Ward, for $12,875. This area, located along the East River waterfront, is now known as the DUMBO Historic District (an area now bounded roughly by the Brooklyn Bridge, the East River, York, and Navy Streets). Although this area was one of the first residential-use sections of Brooklyn, by 1852 it was well on its way to becoming a major manufacturing center, with factories, foundries, and warehouses vying for space with two and three-story residential houses. Two ferry lines, one right at the foot of Front Street, made regular trips to and from New York City.
In 1853, Seabury sold this property for $15,500. In one and a half years, he made a profit of $3,500.
… and Fort Greene
In 1858 and 1859, Seabury added to his Brooklyn holdings with the purchase of nine lots, some with buildings, on Fulton Avenue, Raymond Street, and Navy Street, in the 11th Ward (now the Downtown Brooklyn/Fort Greene area), for $12,000. The property was advertised in the Evening Post in 1850 as being “located in the most desirable part of Brooklyn, being in the immediate vicinity of Washington Park, which is now being regulated and graded.” He immediately sold two of the lots for $4,600. In 1863, he sold four of the lots for $15,500, making a profit on land he had owned for only four years.
With the growth of middle-class residential districts, including Fort Greene, house construction in Brooklyn skyrocketed. Row houses appeared almost overnight on the quiet streets, and became ideal homes for professionals who commuted to their New York City businesses. According to Seabury’s personal ledger, he spent a great deal of money building on his Brooklyn properties. Between July and October 1863, for example, he paid John P. Seeley (a “master builder,” according to the 1860 Federal Census) $9,370, most likely for house construction. Seabury also paid $102.31 to have a sidewalk laid on his property on Raymond Street.
The Good Son-in-Law
Effingham Nichols, an attorney and the husband of Seabury’s eldest daughter, Elizabeth, must have been influential in Seabury’s decision to invest in Brooklyn real estate. He lived in Fort Greene with his wife and daughter, Lillie, from 1859 to 1864, and had begun to buy property there in 1851; by 1859 he owned at least seven properties in the neighborhood. (See my post of April 2017, “Days of Sorrow, Days of Rejoicing”). In addition, one of his brothers, William B. Nichols, owned houses near Seabury’s property on Fulton Avenue and Raymond Street. Effingham may have collected rents for Seabury, and may even have acted as an agent for him, buying and selling properties at his discretion. Records in Seabury’s personal ledger indicate that Seabury provided Effingham with funds to repair the Fulton/Raymond Street property. In 1863, for example, he gave Effingham $63.84 for sewer work.
In 1863, Seabury made what may have been his last purchase of Brooklyn real estate, bidding at auction for another parcel of land in Fort Greene, paying $4,400. The Land Conveyance Records Index for Kings County indicate that Seabury purchased at least three other properties in Brooklyn; the details of these purchases could not be determined because the conveyance records are missing.
Seabury the Landlord
Seabury also collected rents on some of his properties. In 1862, he rented three buildings on Fulton Avenue to Mary Louise Tredwell (a distant cousin) for $1,200/year. Seabury’s personal ledger indicates that in 1852 he was collecting rent of $1,000/year on a factory on Front Street, and $212.50/year for a Pearl Street property.
Seabury also engaged in seller financing, wherein he financed purchases of his property to individuals, rather than have them obtain a bank mortgage. In his personal ledger, he listed several individuals to whom he sold property, such as John and William Healy, John Rupp, and John David, and the amounts of the mortgages he granted.
Ventures Further Afield
Records show that Seabury also invested in commercial property with his partners for their business. Seabury and his nephews likely decided to invest in real estate in North Carolina due to their business dealings there and their familiarity with the state. Seabury’s eldest brother, Samuel Tredwell (1763-1827), had been a prestigious figure in North Carolina after the Revolutionary War. In 1785, Samuel moved to Edenton, North Carolina, whose vital port was the second largest in the state. In 1793, he was appointed Collector of the Port of Edenton by President Washington, a position he held until his death. He also served as State Commissioner of North Carolina in 1818.
In 1835, Tredwell, Kissam & Company purchased 13,000 acres of North Carolina swampland from Charles Johnson for the purpose of harvesting lumber to make shingles. A North Carolina Supreme Court case in June 1840 involved a lawsuit brought against a trespasser who was using the land illegally. At this time it is unknown when and to whom Seabury sold the land.
In the Transactions of the Supreme Court of the Territory of Michigan, 1825-1836, there is a record of a court case involving Tredwell, Kissam & Company in a lawsuit against three men, Isaac Otis, George Walker, and John Hale. The nature of the suit is unknown.
The Children Benefit
A portion of the original property on Fulton Avenue and Raymond Street in Brooklyn was still under Seabury’s name upon his death in 1865, and became part of his estate. His children benefited from Seabury’s real estate savvy. In 1902, Samuel Lennox, his younger son, who had purchased the Fulton Avenue property from his father’s estate some years earlier, sold it for $40,200. The property was described in a February 1902 advertisement in the Brooklyn Eagle as “being a very valuable plot with three two story and cellar brick buildings thereon, with 5 stores therein.”
Seabury’s Investment Portfolio
It is unclear when Seabury set about building an investment portfolio, but by his death in 1865 he had amassed enough stock to significantly cushion his family’s inheritance. Getting in on the ground floor of both the steam engine and lighting revolutions taking place in New York City and elsewhere, he invested heavily in various railroad stock (including the New York and Erie Line, the Hudson Line, Chicago and Rock Island lines, and Hartford and New Haven lines) and in gas lighting. Seabury may have consulted his friends and former colleagues in the business world for advice; he also may have looked to his sons-in-law Effingham Nichols and Charles Richards for guidance in choosing his investments.
The New York and Erie Railroad Line
Seabury Tredwell was an early investor – and possibly one of the original investors – in the New York and Erie Line, a railroad that linked Erie Canal towns directly to New York City, allowing for faster transportation of lumber and agricultural goods. Leading merchants of the day, as well as land investors and bankers, were granted the charter in 1832, creating a railroad line that ran west from the Hudson River in Piermont, New York, to Dunkirk on Lake Erie. This proved to be a risky investment through the years, however; the railroad went bankrupt several times, and became known as “the scarlet woman of Wall Street,” due to the financial shenanigans of men like Jay Gould and Cornelius Vanderbilt, who vied for control of the railroad and manipulated the company holdings to their own advantage.
Take the Hudson River Line
The Hudson River Line was another of Seabury’s investments. In 1846, 11 years after Seabury sold his business, the Hudson River Line was chartered. This commuter line initially ran from Chambers and Hudson Streets in lower Manhattan up the West Side via horse cars (steam trains were not permitted below 30th Street) to a depot at 32nd Street, where the horses were exchanged for steam engines, then along the east side of the Hudson River, to Peekskill. By 1851 it had been extended to Poughkeepsie, which remains its terminus. Through a connection with the Troy and Greenbush Railroad, it provided a link between Albany and lower Manhattan, a trip of less than four hours. A similar journey by steamboat took over seven hours! One imagines that the growth of the railroad industry (with its speed, efficiency, and convenience) and its revolutionary impact on 19th century life was not lost on Seabury, who, like everyone else, had previously relied on the comparatively snail-paced omnibuses, ferries, and coaches.
New York Gas Light Company
Seabury’s personal ledger indicates that he owned 133 shares of stock in the New York Gas Light Company, the first coal gas company in New York, founded in 1823. One wonders if he was one of the original investors in the company, which first focused on street lighting, servicing Manhattan south of Canal Street. Ultimately six gas companies supplied gas for illumination and later, for heating and cooking. The competition for customers was so fierce in the growing city, that workers from different companies would do battle in the streets over the installation of gas mains; known as “gas house gangs.” In 1884, the companies merged to form Consolidated Gas Company (now known as Con-Edison).
More than a Merchant
Now that Seabury’s varied business interests have come to light, and we see the extent to which he ventured into unchartered investments, it is clear the title “merchant” doesn’t embrace all that Seabury was in the business world of the 19th century. Seabury Tredwell, along with many of his peers in the merchant class, were men of opportunity who shaped the economic future of New York City. Perhaps we should consider renaming the Merchant’s House — the “Investor’s House”? The “Risk-Taker’s House”? What do you think?
Sources:
- Blume, William Wirt, ed. Transactions of the Supreme Court of the Territory of Michigan 1825-1836, Volume II. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press, 1940. www.babel.hathitrust.org. Accessed 5/29/19.
- Bristed, Charles A. The Upper Ten Thousand: Sketches of American Society. New York: Stringer and Townsend, 1852. www.babel.hathitrust.org. Accessed 6/5/19.
- Brooklyn Citizen. April 2, 1902, p. 9. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 5/3/19.
- Brooklyn Daily Eagle. February 22, 1902, p. 15. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 5/3/19.
- Burrows, Edwin G. and Mike Wallace. Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Conveyances, 1724-. New York Land Records, 1630-1975. Images. familysearch.org.
- “Erie Railroad Company.” Encyclopedia Britannica. www.britannica.com. Accessed 6/3/19.
- Evening Post. October 5, 1850, pg. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 5/22/19.
- “History of Con Edison.” American Oil & Gas Historical Society. www.aoghs.org. Accessed 6/3/19.
- Koeppel, Gerard. City on a Grid: How New York Became New York. Boston: Da Capo Press, 2015.
- Lockwood, Charles. Manhattan Moves Uptown: An Illustrated History. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1976.
- New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission. DUMBO Historic District Designation Report. December 18, 2007. www.neighborhoodpreservation.org. Accessed 5/21/19.
- New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission. Fort Greene Historic District Designation Report. September 26, 1978. www.home2.nyc.gov. Accessed 5/22/19.
- New York Daily Herald, March 11, 1865, p. 2. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 6/9/19.
- North Carolina. Supreme Court. North Carolina Reports: Cases Argued and Determined in the Supreme Court of North Carolina, [v 023, June Term 1840-June Term 1841]. State Library of North Carolina. www.digital.ncdcr.gov. Accessed 5/29/19.
- Notes from Seabury Tredwell’s Personal Ledger Book. Merchant’s House Museum Archives.
Meet the Tredwells: Seabury Tredwell, Part 2 – The Merchant Years
by Ann Haddad
A Knack for Success
Throughout his life, Seabury Tredwell had a remarkable knack for being in the right place at the right time. Or perhaps he had wise advisors who guided him carefully. However he made his decisions, they seemed to always be the right ones. He arrived in New York City to make his fortune as its wealth and reputation as a great commercial center was about to explode; thirty-five years later, he ended his mercantile career and moved uptown, narrowly escaping the Great Fire of 1835 and the economic Panic of 1837. He knew the chic neighborhood to move to and the finest country property to buy. The story of his trajectory from country farm boy to elite New York merchant is a classic success story.
Enter Seabury
Seabury arrived in New York City sometime around 1800, when the city’s population was approximately 60,500. Probably working initially as an entry-level clerk, he became one of approximately 1,100 merchants who aspired to achieve success in the growing city. He either lived with his boss (clerks often slept on the store premises), or took lodging in a boarding house. He most likely packed all of his possessions into one trunk; its contents may have been similar to that brought by a young clerk in “The Perils of Pearl Street,” : “Two pair of stockings, one vest, one pair of pantaloons, one dress-coat, two nightcaps, three cravats, one pair of boots, and one pair of slippers.” No doubt Seabury was given a sum of money by his father or another relative to tide him over financially until he was self-sufficient. For more information about Seabury’s arrival in New York City, see Meet the Tredwells: Seabury Tredwell, Part I – The Early Years.
“The Commercial Emporium of America”
With the end of the War of 1812, the lifting of British blockades, and the subsequent restoration of trade, the Port of New York began the steady economic growth that eventually led it to become the world’s busiest seaport. According to The Rise of New York Port (1939), the years from 1815-1865 saw the seaport’s greatest development into “the commercial emporium of America.” Several factors contributed to this intense and rapid growth.
The Black Ball Line
The launching of the Black Ball Line in 1818, whose four ships made regularly scheduled voyages to and from Liverpool, allowed New York to ramp up its importing of foreign goods, beating out the competitive port cities of Boston and Philadelphia. On average the packets travelled from New York to Liverpool in 23 days; the reverse trip west could take anywhere from 45 to 90 days, depending on weather and wind conditions. Due to the success of the Black Ball, other lines soon followed suit and, according to Gotham (1999) by Burrows and Wallace, by 1838 52 packet ships were shuttling from New York to Liverpool. The development of inland steamboat service by 1817 also contributed to traffic between the city and Long Island Sound and the North (now Hudson) River. Imagine the East and North River wharves lined daily with nearly 1,000 steamboats and packets!
An Ideal Harbor
The joining of the East and North Rivers created a large harbor that was ideal for foreign and domestic commercial trade. Owing to its location and tides, the harbor was well sheltered and free of the treacherous ice that could damage ships, and therefore its ports were accessible in all seasons. The depth of the water allowed large ships to come close to the wharves to load and unload cargo.
The Erie Canal – “Clinton’s Ditch”
The opening of the 363-mile Erie Canal in 1825, which connected the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes via the Hudson River, galvanized commerce and enabled New York to become the gateway to the rich agricultural resources of the Midwest. Those who opposed the plan to build the canal referred to it as “Clinton’s Ditch,” to ridicule Governor DeWitt Clinton, who was one of the major supporters of the project. Its route from New York City to Buffalo allowed midwestern markets to receive highly desirable imported manufactured goods; in return, domestic produce grown in the nation’s interior could be shipped (at a dramatically lower cost) to the New York markets. This exchange of more and more goods took significantly less time, increasing the velocity of trade in New York dramatically.
As a result of the surge and speed of trade, a new way of doing business developed in New York. Merchants sought ways to store the wealth of goods coming in and going out, while also selling them directly to consumers. The brick warehouses constructed for this purpose, which forever altered the landscape of Lower Manhattan, typically held a store/living space on the ground floor with storage areas above. The ubiquitous cart man transported the goods from the teeming wharves to the shops, where they would be hauled up by ropes to the second and third floor.
The Merchant Class
As New York’s commercial activity accelerated with each passing year, the wealth of the city and its merchants grew to unprecedented heights. According to the Commercial Directory (1823), in 1820 the value of goods imported into New York City was $26 million, and the value of exported foreign merchandise and domestic goods was nearly $12 million. The men who controlled the mercantile business became powerful and wealthy in the process and were known as the elite “Merchant Class.” Individually, those who could claim membership in this group were later referred to as “Merchant Princes.” Seabury Tredwell was indeed deserving of this distinction.
The Hardware Trade: Seabury’s Niche
We do not know if Seabury was set on becoming a hardware merchant from the start, or if he clerked for a merchant in the hardware trade, during which time he learned the details of the business. According to John C. Tucker, a New York City hardware merchant whose career overlapped with Seabury’s for several years, in the first half of the 19th century, “American Hardware was almost unknown.” Seabury purchased his goods from importers and wholesaled them from his warehouse. During his years in the hardware trade, more than 85 percent of the goods Seabury sold were imported. According to Tucker, the only American-made hardware was cut nails, and even those Seabury’s company also imported (see advertisement at right). Hence Seabury and other businessmen relied heavily on the merchant ships to deliver their goods in a timely fashion. Severe weather or a shipwreck could be a major setback to business.
It should be noted, however, that some percentage of the goods Seabury sold were American-made. At the bottom of an Evening Post advertisement (September 6, 1816), he added, “ALSO, Many articles of American Manufacture in the Hardware line.”
Trade Embargo
From his shop and warehouse on Pearl Street (see previous post for shop locations), Seabury set to work building his business and reputation as a hardware merchant. His career may have been derailed for several years during the trade embargo imposed by President Thomas Jefferson from December 1807 to March 1809, which prohibited American ships from trading in foreign ports. As a result of this effort to protect American shipping rights and to maintain neutrality amidst the raging Anglo-French conflict, activity at the seaport came to a standstill. The export trade declined by nearly 80 percent; imports by 60 percent. Many mercantile firms went out of business and unemployment among seaport workers skyrocketed. The embargo may explain the absence of Seabury’s name from the city Directory in 1808; like many other merchants, he may have had to close his business. Once the Embargo Act was repealed by Congress, in March 1809, Seabury’s name once again appeared in the Directory.
All in the Family
According to hardware merchant John C. Tucker, a “large business” was one that sold between $150,000-$200,000 worth of goods per year. Although the size of Seabury’s business is unknown, by 1815 his wealth had grown to such an extent that he took on his nephew, Joseph Kissam, as a partner, naming the firm Tredwell & Kissam. Joseph’s brother, Samuel, would join them three years later; the firm then became known as Tredwell, Kissam, and Company, and remained so until Seabury’s retirement in 1835. The partners typically shared equally in the responsibilities and profits of the company.
In The Old Merchants of New York (1863-66), author Joseph A. Scoville notes that bringing family members into the business was almost de rigueur. A merchant on the road to success “does not rest until one by one he has procured situations for all of his brothers” (or in Seabury’s case, nephews). Joseph (1790-1863) and Samuel (1796-1856), were the sons of Seabury’s sister, Elizabeth (1767-1803), and her husband Dr. Daniel Whitehead Kissam (1763-1829), of Hempstead, Long Island.
Newspapers: The Way to Advertise
Although they did some some retail business in the stores attached to their warehouses, (Seabury’s advertisements occasionally indicated that items may be purchased “from the shelves”), companies like Tredwell, Kissam and Company worked largely in wholesale. To keep his customers apprised of the goods arriving from England, Seabury advertised in the newspapers, paying a subscription of $40 per year to advertise at will, but typically three or four times a year, based on the packet schedule. (According to The Old Merchants of New York, “no respectable house would overdue the thing. [over-advertise]”). Country merchants, who would come into town several times a year to make their purchases (typically in the spring and fall), consulted the advertisements to determine which houses to visit. With these personal interactions, merchants would establish relationships with their clients, and come to understand their financial situations; this usually ensured customer loyalty, especially if the merchant extended credit to the customer when necessary.
Seabury Tredwell’s first newspaper advertisement appeared on September 7, 1812. He advertised 30,000 musket flints (a form of quartz used to ignite firearms), and pistols. Tredwell & Kissam’s first advertisement appeared on August 16, 1816. As this was one year after Seabury took on a partner, it may indicate a deliberate decision on Seabury and Joseph’s part to expand the scope of their business. The ad boasts of the company’s “extensive assortment” of goods, and stress that they offer “liberal terms” for both retail and wholesale “by the package, or in quantities to suit the country trade.” In addition to hardware such as cutlery, waffle irons, tools, and cookware, the company also sold looking glasses, buttons, and ladies’ pocket books.
Newspapers like the Evening Post also regularly printed notices of ships’ arrivals in New York Port. On November 2, 1815, the ship Zodiac arrived after a 70-day voyage from Liverpool, England, bearing cargo for Tredwell & Kissam. These notices would then typically be followed by advertisements from the company announcing the goods they now had in stock.
A Pearl of A Street
Prior to the Civil War, the mile-long stretch of the East River from the Battery to Corlear’s Hook (now at Cherry Street and the East River Drive), was home to the busiest wharves. Because of their proximity to the waterfront, where ships loaded and unloaded their cargo, streets such as Pearl, (especially the blocks north of Wall Street and south of Fulton), Front, South, Wall, Pine, and lower Broadway comprised the epicenter of commercial activity. Hundreds of merchants had their shops and warehouses on these streets. According to the Commercial Directory (1823), on Pearl Street alone, 90 mercantile firms vied for customers, selling everything from dry goods and cotton to china and fine jewelry. Auction houses were plentiful as well. Tredwell, Kissam and Company was one of eight hardware merchants on Pearl Street that year.
Seabury’s Daily Routine
Whether he ventured to his warehouse on Pearl Street from his boardinghouse a short distance away, or later from his home on Dey Street, when he had to walk a few blocks further, Seabury’s daily routine probably resembled the one described in The Old Merchants of New York:
“To rise early, to get breakfast, to go down to the counting house of the firm, to open and read letters – to go out and do some business…until twelve, then to take a lunch and a glass of wine at Delmonico’s; or a few raw oysters at Downing’s; to sign checks and to attend to the finances until half past one; to go on change [the Merchant’s Exchange]; to return to the counting house, and remain until time to go to dinner, and in the old time, when such things as packet nights existed [when the packet ships would arrive at port], to stay down until ten or eleven at night, and then go home and go to bed.”
Rising Stars
Tredwell, Kissam, and Company achieved great success in the hardware business. From their early days, they cast a wide net to acquire customers. Records indicate that, in addition to New York, they did business in Connecticut, Philadelphia, Massachusetts, and Michigan.
On September 19, 1812, a storekeeper in New Milford, Connecticut, named Elijah Boardman paid $28.31 to Seabury Tredwell for goods, including “three dozen barber knives, 1 dozen teaspoons, and 1 dozen dustpans.”
Another undated bill of $3.56 to Elihu Harrison of Morris, Connecticut, from Tredwell, Kissam, and Company, was for “steel knitting pins and thimbles.”
On November 22, 1827, the shop of William & Fairchild in Stockbridge, Massachusetts, ordered “brushes, spoons, thimbles, violin strings, steel traps, curry combs, sad irons, trace chains, etc.” from the firm.
As his business grew, Seabury and his partners continued the tradition of hiring clerks to do the daily work of the company while learning the trade. William Floyd-Jones, from Oyster Bay, Long Island, started out in 1831 as a clerk for “the highly respected wholesale hardware house of Tredwell, Kissam and Co.” and became a member of the firm in 1837, retiring in 1855.
Trade Tokens
Trade tokens were often used by businesses either to provide sufficient currency during times of coin shortages (especially when stores were in remote locations away from banks), to extend credit, or as a form of advertising, to let potential customers know their location and the services and goods available. In 1823, and again in 1825-26, Tredwell, Kissam and Company issued trade tokens, struck by Kettle & Sons of England, to commemorate the opening of the Erie Canal, referred to on the coin as the “Grand Canal.” According to Robert D. Leonard, a collector of trade tokens, most of the pieces made for commemoration saw limited circulation as money.
.
.
.
The South Beckons
Seabury did not limit his business to the New England or Mid-Atlantic states. Like many other merchants who realized the huge market for goods in the South, he did business with and extended credit to storekeepers in Alabama and the Carolinas. As early as 1816, Tredwell & Kissam was advertising in Southern newspapers. In an advertisement placed in The American (Fayetteville, North Carolina) on October 17, 1816, they advertised hardware and cutlery “to suit the country trade.”
Typically, a traveling salesman, or “drummer,” would venture to faraway cities to provide catalogs, collect orders, and in many cases, settle overdue accounts. In a letter to Tredwell, Kissam & Company dated January 11, 1831, from a Montgomery, Alabama, storeowner named William Shute, he references a “Mr. Smith,” who was apparently a drummer for Tredwell, Kissam, and Company: “…your Mr. Smith left here a few days ago. He said you have a fine stock of guns and Memo to order. Below we hand you an order for such goods as we are in immediate want of which you will please ship by 1st vessel for Mobile.” Shute goes on to list the desired goods, including guns, corn mills, and padlocks.
Tredwell, Kissam and Company must have had strong commercial ties to North Carolina, for in 1831 they donated $100 towards the relief of citizens of the city of Fayetteville, after a disastrous fire that took place there on May 29.
.
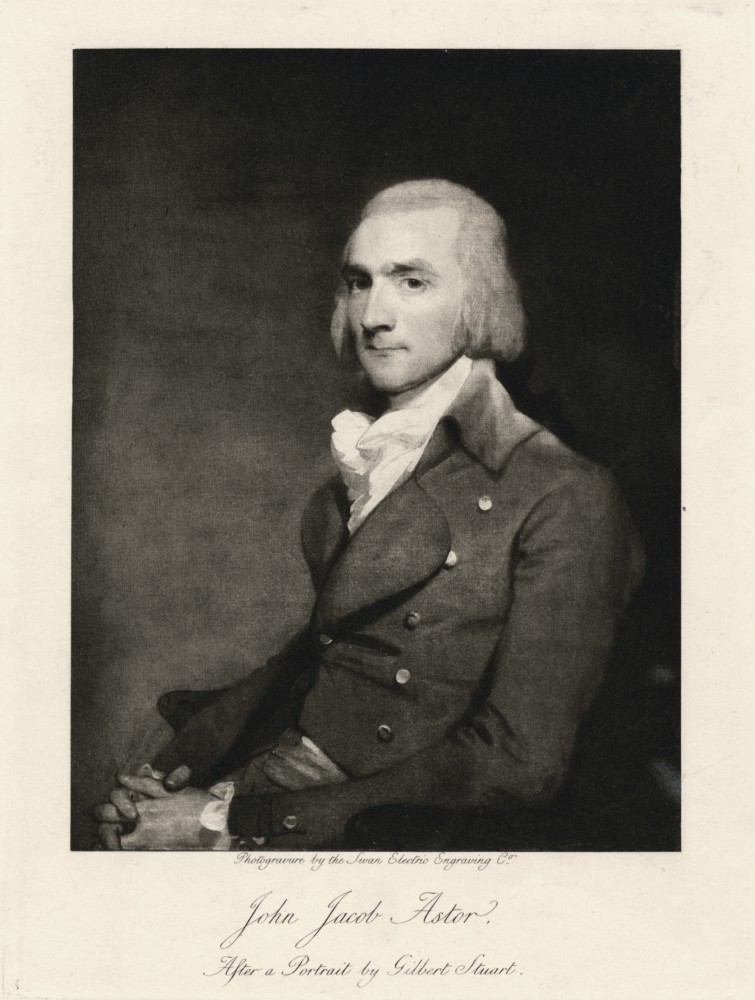
A Famous Client
Undoubtedly the most famous client of Tredwell, Kissam, and Company was John Jacob Astor (1763-1848), the German-born fur trader and real estate investor who at his death was the wealthiest man in America, with a fortune worth approximately $20 million. Records of Astor’s American Fur Company indicate that he purchased guns from Tredwell, Kissam, and Company in 1832 and 1833, for use in trade with Native Americans in exchange for furs. In a “Memorandum of Guns to be Furnished,” dated October 31, 1832, Astor gives very specific instructions as to the quality of the guns, indicating that a previous shipment had been of less than desirable quality:
“The stocks of many of the guns you gave us last spring were made of two pieces of wood united at the gap … This must not on any account be the case with the present order…Our Indians consider them not new, but old arms patched up, and in numbers instances have returned them to our traders, [illegible] them with having practiced an imposition, by selling them a mended article for one that was new and perfect in every respect. The pernicious effect of such an impression is of too much importance to our interest to be overlooked.”
The Memorandum stipulates that the specific order of 410 guns must be “ready for delivery” by April 10, 1833, which gave Tredwell, Kissam and Company six months to import the guns from England, then pack and deliver them. This order indicates the long turnaround time from ordering to acquisition and delivery of goods.
Guns and Cotton Trade
The above-mentioned orders from Shute and Astor point to a shift from hardware to guns on the part of Tredwell, Kissam, and Company. Although America was beginning to manufacture guns in small amounts (Derringer in 1810, Remington in 1816, and Colt in 1836), by 1815 the British were mass-producing millions of guns per year; Seabury’s company relied on overseas production to readily fill their large orders. The English fowling gun, used to hunt birds and fowl, was made in Birmingham, England, and was primarily sold to Native Americans.
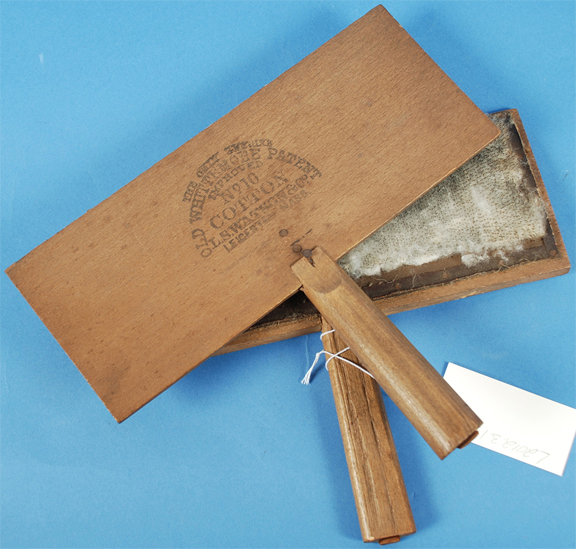
Although Seabury’s company did not engage in the rapidly growing cotton industry on a large scale (by the mid-1840s, cotton accounted for almost 45 percent of the gross national product), they did sell items that supported the trade, and, in at least one instance, sold cotton. In an advertisement in the Evening Post (December 23, 1819), the company offered “7 bales Cotton (new crop), landing from sloop Cashier.” This appears to be a one-time venture, however. What Seabury did sell in considerable quantities were cotton cards, tools used to process raw cotton in small amounts for lower-scale production. The cards disentangled and cleaned the raw cotton fibers after the cotton was picked. He also occasionally sold hemp cotton bagging, which was used to pack bales of cotton.
A Rich Man
In 1822, Lanier’s A Century of Banking in New York, 1822-1922 (1922), included Seabury in a list of “The Rich Men of 1822,” wherein the value of his personal property, from 1815 to that date, was listed as $17,500. This was quite a significant amount of money for that time, especially considering that it references only Seabury’s personal property. Seabury was living in the boardinghouse during those years, so this amount represents the value of his business and whatever chattel he owned. The real property he owned at that time (Seabury’s real estate ventures will be discussed in the next post) was not included in this estimate.
A Prince among Princes
On January 11, 1834, one year before his retirement, Seabury was a pallbearer at the funeral Thomas Seaman Townsend (1771-1834), held at St. George’s Episcopal Church (then located on Chapel Street, now Beekman), where Townsend was a vestryman. Townsend was a wealthy merchant who was a neighbor of Seabury’s on Dey Street. The names of pallbearers who joined Seabury that day reads like a list of merchant elite of New York, including such highly regarded men as Benjamin Strong, Anthony Underhill, and Stephen Van Wyck.
The End of an Era
On February 4, 1835 the following notice appeared in a New York newspaper, indicating the end of a 20 year partnership:
“The firm of Tredwell, Kissam & Co. is dissolved by mutual consent. Seabury Tredwell and Samuel Kissam retire. Either of the Partners will attend to the settlement of the business, at 228 Pearl-street.” [Signed] Seabury Tredwell, Joseph Kissam, Samuel Kissam New-York, January 31, 1835.”
The same day, Joseph Kissam announced that he had formed a new partnership with James A. Smith and William Bryce, and would continue the hardware business under the name Kissam & Co.
Although Seabury was only 55 years old when he retired, he had been in the hardware business for many years, roughly from 1800 to 1835. That is a long career by any standard. After such an extended, successful run, it is no wonder Seabury decided to retire. And no doubt he trusted that his nephew Joseph would continue the business he had worked so hard to establish.
A New Life Uptown
On October 31, 1835, Seabury sold his home on Dey Street to his former partner Joseph Kissam for $10,000. Two days later, he purchased a new home at 361 Fourth Street, for the hefty sum of $18,000. The seller was Joseph Brewster, a hatter and real estate speculator, who had built the late-Federal and Greek Revival row house three years earlier. Seabury, with his wife, Eliza, and seven children, bid farewell to the hustle and bustle of lower Manhattan, and moved to the elite Bond Street neighborhood. Thus began Seabury’s retirement, and another chapter in the life of this wealthy New York merchant.
Sources:
- Account of William & Fairchild. William B. Pennebacker Watermark Collection, 1710- ca. 1936. The Joseph Downs Collection of Manuscripts and Printed Ephemera. Winterthur Museum. findingaid.winterthur.org: Box 3, Folder 15.
- Alabama State Archives. Record Book of William Shute, of Shute and Hackett, 1834-1837.
- Albion, Robert Greenhalgh. The Rise of New York Port [1815-1860]. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1939.
- The American. October 17, 1816, p. 1. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 4/16/19.
- Atherton, Lewis E. “The Problem of Credit Rating in the Ante-bellum South.” The Journal of Southern History. Vol. 12, No. 4 (Nov., 1946), pp. 534-556). www.jstor.org. Accessed 3/17/19.
- Atherton, Lewis E. “Predecessors of the Commercial Drummer in the Old South.” Bulletin of the Business Historical Society. Vol. 21., No. 1 (Feb., 1947), pp. 17-24. www.jstor.org. Accessed 3/18/19.
- Barrett, Walter [pseud.] [Scoville, Joseph A.]. The Old Merchants of New York City. New York: [various publishers]: 1863-1866. www.archive.org. Accessed 4/28/19.
- Black, Samuel W. “Tools of Oppression: Cotton Cards.” Collection Spotlight at the Heinz History Center Blog. www.heinzhistorycenter.org. Accessed 3/17/19.
- Burrows, Edwin G. And Mike Wallace. Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Calendar of the American Fur Company Papers. Orders Outward, Volume 2, 1827-1833. Manuscript Collections, New-York Historical Society.
- Commercial Directory, Containing a Topographical Description…” Philadelphia: J.C. Kayser & Co., 1823.
- Davenport, Linda Haas. Haas/Davenport Homepage. www.lhaasdav.com. Accessed 3/18/19.
- Elihu Harrison Papers, 1812-1836. Litchfield Historical Society.
- Elijah Boardman Papers, 1782-1853, Litchfield Historical Society.
- Evening Post. September 11, 1812, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 5/6/19.
- Evening Post. November 2, 1815, p. 2. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 7/23/15.
- Evening Post. August 16, 1816, p. 4. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 7/23/15.
- Evening Post. December 23, 1819, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 4/28/19.
- Evening Post. March 3, 1824, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 7/23/15.
- Evening Post. April 4, 1832, p. 1. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 7/23/15.
- Fayetteville Weekly Observer. November 16, 1831, p. 2. www.newspapers.com. Accessed May 25, 2017.
- [Green, Asa}. The Perils of Pearl Street, Including a Taste of the Dangers of Wall Street. New York: Betts & Anstice, 1834.
- “John C. Tucker.” The Iron Age: A Review of the Hardware, Iron, and Metal Trades. Volume 49, February 18, 1892, pp. 321-22. New York: David Williams. www.babel.hathitrust.org. Accessed 4/23/19.
- Lanier, Henry W. A Century of Banking In New York, 1822-1922. New York: G.H. Doran Co., 1922.
- Leonard Jr., Robert D. “Collecting U.S. Tokens: Challenges and Rewards.” Chicago Coin Clu, 1986. wwwchicagocoinclub.org. Accessed 4/26/19.
- Minutes of the Common Council of the City of New York, 1784-1831.New York: The City of New York, 1917. www.archive.org. Accessed 3/1/19.
- Newtown Register, Thursday, February 13, 1896: www.fultonhistory.com. Accessed 3/12/19.
- New York Land Records, Conveyances, 1835-36 vol. 343-345. www.familysearch.org.
- Public Documents Printed by Order of the Senate of the United States, Volume II. United States Congressional Serial Set, Volume 239. Washington, D.C.: December 1, 1834. www.books.google.com. Accessed 3/18/19.
- Sells, Steve. Traditional Muzzleloader. www.traditionalmuzzleloader.com. Accessed 5/4/19.
- Shipping and Commercial List and New-York Price Current. February 4, 1835, p. 3. America’s Historical Newspapers. www.newsbank.com. NYPL. Accessed 6/29/17.
- Townsend, Margaret. Townsend-Townshend, 1066-1909. New York: [Press of the Broadway Publishing Company], p. 107. www.babel.hathitrust.org. Accessed 4/23/19.
Meet the Tredwells: Seabury Tredwell, Part 1 – The Early Years
by Ann Haddad
A Revolutionary Birth
When Seabury Tredwell was born in the village of Hempstead, Long Island, on September 25, 1780, his family and other members of his farming community were in the midst of the suffering and havoc caused by the ordeal of seven long years of British occupation during the American Revolution. The countryside had become one large British military camp, and residents (both Patriot and Loyalist) saw their property confiscated, their rights disregarded, and their families divided. No doubt an air of disillusionment and disorder pervaded the village; this continued for a time after the war ended in 1783 and the unimaginable had occurred: the Patriots had defeated the fearsome British Army. As Hempstead began to rebuild and restore its land and shattered village, as the new order of government was formed, and as the animosity that had severed family ties abated, Seabury Tredwell, a future “merchant prince” of New York City, was growing up.
A Classical Education
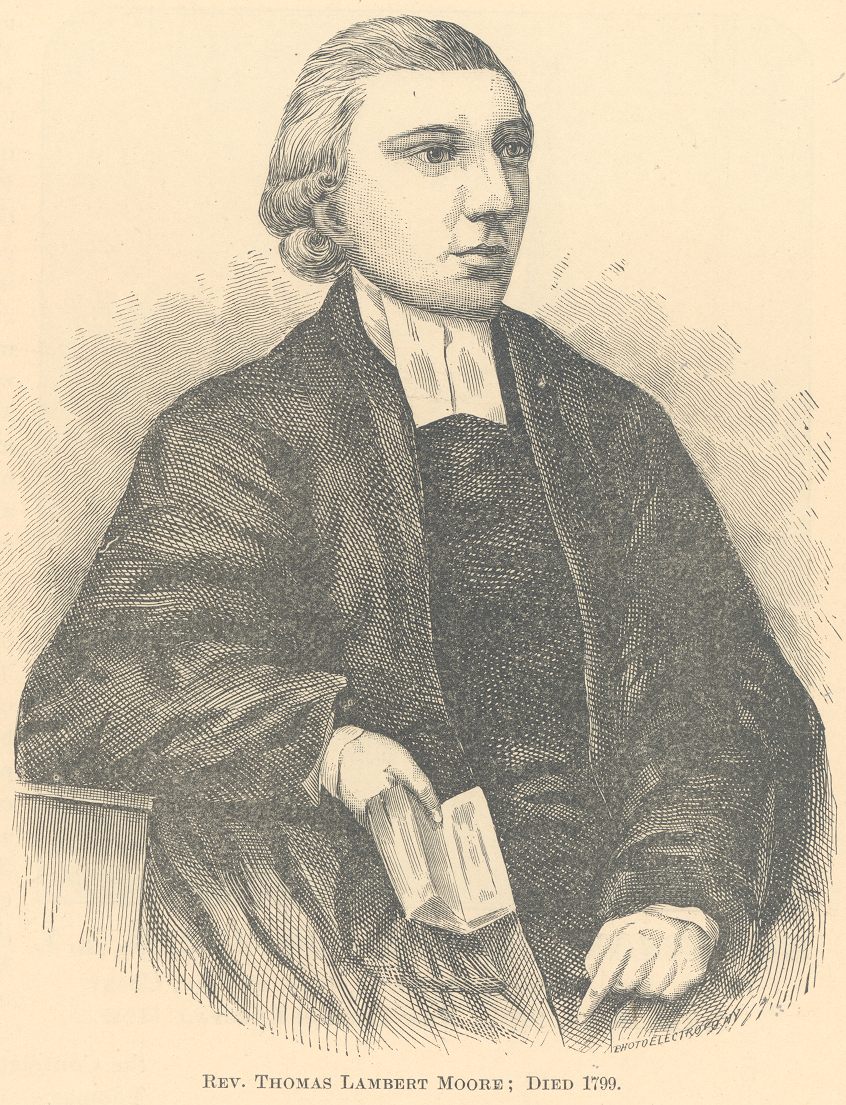
Seabury’s parents, Dr. Benjamin Tredwell and Elizabeth Seabury Tredwell, most likely decided to send their son to the school in Hempstead begun by Elizabeth’s father, Reverend Samuel Seabury (1706-1764). Reverend Seabury became rector of St. George’s Church in Hempstead in 1743; to compensate for the inadequate salary the position provided, he opened the school sometime around 1762. According to an advertisement on March 27, 1762, in the New York Mercury, the annual tuition of 30 pounds sterling included room and board, as well as “washing and wood for school-fire.” Housed in the rear of the parsonage, the school acquired an excellent reputation over the years, while providing a classical education to the children of notable New York families and Tredwell relatives, including the Onderdonks and the Kissams. During Seabury’s school years, the rector of St. George’s (and likely Seabury’s teacher) was Reverend Thomas Lambert Moore (1758-1799).
Move to the Big City
It is uncertain when Seabury moved to New York City to begin his adult life and start a business. Most likely, he arrived in New York City sometime between 1798 and 1801, when he was between 18 and 21 years old, and had “come of age.” An obituary (source unknown), published at his death in 1865, notes that, “He came to this city in 1798 [he would have been 18 years old] and after serving as a clerk for three years started the hardware business on his own account.”
Two of Seabury’s older brothers had preceded him and were established as merchants by the time he arrived on the scene. Adam Tredwell (1772-1852), who became a hugely successful fur merchant, first appeared in the Directory 1795 as a partner in Tredwell & Thorne, on 21 Burling Slip, when he was 23 years old. John Tredwell (1775-1851) appeared in 1796 as a china and glassware merchant on 197 Water Street. He was 21 years old. Both men may have arrived earlier and clerked for others before becoming merchants in their own right.
Merchants and their families often shared living quarters with their employees “above the store.” As a clerk, Seabury may have lived in the shop of his employer; it is unclear if he would have been listed in the Directory as such. His two older brothers married in 1801, and it is doubtful that Seabury lived with them for any length of time. He is not listed in the 1800 Federal Census (the Census only listed the head-of-household and number of residents at each address); his name does not appear in the Directory until 1803, where he is listed as a merchant at 260 Pearl Street. He was 23 years old at that time.
Yellow Fever Strikes
Seabury’s arrival in New York City may have been delayed by the appearance of the worst yellow fever epidemic in New York City history, in August 1798. It continued through late October, claiming 2,086 victims. Residents fled the city in hope of escaping the scourge. Seabury did not turn 18 until September 25 of that year; he surely waited for the epidemic to subside before moving to the city. The death of his first cousin, James Tredwell, on October 8, 1798, likely caused great consternation among Seabury’s family, discouraging him from leaving Hempstead. James was a physician who died at the age of 30 while treating yellow fever victims.
Seabury Tredwell, Volunteer Fireman
In 1805, two years after his first listing in the Directory, Seabury’s name again appeared in the public record. In the Minutes of the Common Council of the City of New York, May 20, 1805, it is noted:
“Gurdon Manwaring, Seabury Tredwell and John L. Embree were appointed firemen of Company No. 18, instead of Alsop Hunt, Sands Ferris and Edmund Fanning resigned.”
Seabury became a fireman during the volunteer era of firefighting; firefighting in New York City did not become a salaried position until 1865. New York City had established the voluntary New York Fire Department in 1786. The method of fighting fires involved mobilizing the volunteer company (each with 18 “able-bodied, sober men”), to participate in a bucket brigade, in which buckets of water were taken from a well and passed hand to hand to fill the cisterns of the hand fire engine pumps. In 1791, the Common Council passed an ordinance stipulating that each city ward have a designated Fire Warden. The Warden’s role was to examine the houses and buildings in his ward to ascertain that each possessed the required number of leather buckets (one per fireplace). The buckets, with a capacity of at least 2.5 gallons of water, were to be marked with the initials of the landlord (who purchased them at his own expense), and were to be hung by the front door.
| … |
The ordinance also required firemen to:
“at least once a month to exercise with their engines, etc., and to wash, clean, and examine them, under a penalty of six shillings; and for every failure to attend at a fire, and for leaving his engine while at a fire, and for failure to do his duty at a fire, a fine of 12 shillings is imposed, and to be removed from office as a fireman.”
According to Our Firemen: The History of the New York Fire Departments… (1887), Seabury’s Company, Engine Company 18, or the “Union,” was organized in April 1792, and was originally located on John Street, near Pearl Street. In 1813, its location was moved to 228 Water Street, and later to Fulton Street. The company was disbanded in 1828.
By 1805, the year Seabury was appointed Fireman, there were approximately 700 firemen in the ranks. We have no further record of Seabury’s involvement with the New York City Fire Department.
The Seaport Air Turns Sour
As a result of rapid urban growth and increasing commercial and mercantile development by the early 19th century, the lower Manhattan waterfront became an overcrowded, disease-prone, shanty-filled neighborhood that drew residents from all walks of life. The usual custom of living and working in a common space therefore became untenable to affluent gentlemen with families. Living “above the store” was no longer genteel. Adverse to socializing with the lower classes, these men of means sought to separate their homes from their businesses, and sought dwellings in cleaner and safer, i.e., more upscale, residential neighborhoods. Lower Broadway, and the neighborhood to its west, including streets that ran to the North (now Hudson) River, such as White, Barclay, Dey, Warren, and Vesey, became a popular haven for the wealthy. According to Burrows and Wallace in Gotham (1999),by 1810 more than half the merchants or professionals in the Directory listed separate work and living addresses. And, once they left the seaport area, the elite no longer wanted to provide living quarters for their workers.
A City of Boarding Houses
This presented a dilemma for single young men newly arrived in the city. They could neither afford to live in nor did they need an entire house for themselves in more expensive neighborhoods. As a result, the humble boarding house became the solution to their housing needs. These were public establishments (often converted from the former homes of the wealthy who had moved on to more appealing surroundings) that provided room and board for a price; they became a popular living option for men like Seabury Tredwell. Wendy Gamber, in The Boarding House in Nineteenth-Century America (2007), estimates that “between a third and a half of nineteenth century city dwellers either took in boarders or were boarders themselves,” and of the latter, the majority were single young men.
Many boarding houses were located in the center of town, that is, the congested, dirty, mercantile area, near the bustling wharves of the East River. Here the warehouses that could provide employment were nearby, and housing was affordable. Living in a boarding house often brought together men of similar interests; newcomers sat side by side at the dinner table with more experienced residents, who could educate them in the social and work habits of city people, and provide companionship.
We don’t know what Seabury’s rent was during his boarding house years. Gamber states that in the mid-nineteenth century the standard weekly rate for lodging and meals was between $3 and $4, equivalent to approximately $125 today. Seabury, who boarded from approximately 1800 to 1820, most likely paid less.
Widow Williams
The two boarding house owners who figured prominently in Seabury’s story were widows. Widow Susannah Williams, who ran the boarding house where Seabury eventually lived, first appeared in the New York City Directory in 1799, when her establishment was on 31 Lumber Street (now Trinity Place). She subsequently moved to Harmon Street (now East Broadway), then to 263 Pearl Street, in 1805. Seabury’s first location of his hardware business (from 1803 to 1809), was 260 Pearl Street; Mrs. Williams’ boarding house was across the street. Their proximity may be what led them to meet. In 1810, Mrs. Williams relocated to 282 Pearl Street, and two years later, in 1812, Seabury Tredwell was listed at this address in the Directory.
It is noteworthy that in the 1812 Directory, the occupants of Mrs. William’s boarding house are actually listed. Seabury’s name appears, as does his younger brother George Tredwell (1784-1848), who first appears in the Directory in 1805, at the age of 22, at Seabury’s business address of 260 Pearl Street. Perhaps George apprenticed under Seabury; he would eventually join his brother John in the china business.
Due to space and financial constraints, boarders frequently shared rooms with one another. Seabury and his brother George, two of four boarders at Mrs. Williams’ in 1812, probably shared a room (and a bed) when they lived there.
Widow Parker
In 1814, approximately one year after the death of her husband, Seabury’s future mother-in-law, widow Mary Earle Parker, took over Mrs. Williams’ boarding house at 282 Pearl Street. Despite the conveniences of boarding house living, it was nothing like the domestic ideal so beloved in America at this time. In The Physiology of the New York Boarding-Houses (1857), the author states, “A Boarding-House is emphatically, NOT a home.” Having grown up in a large family, Seabury perhaps welcomed the arrival of Mrs. Parker and her four children, including 17 year-old Eliza. He was 34 years old, and had been living as a boarder for approximately 15 years, which was much longer than the average length of stay for single men. According to Kenneth Scherzer in “The Unbounded Community” (1992), “A few people boarded into their late twenties and even into their thirties, but for most, boarding was simply a passing stage of the life cycle.”
Love at 282 Pearl Street
In 1814, when Seabury met Eliza Parker, he was 34 years old, well-established in his lucrative hardware business, and most likely eager to marry. And despite the assertion by the author of Boarders and Boarding House Keepers (1847) that”Landladies are … inevitably cognizant of most of the little meannesses, jealousy, and faults of their boarders – for in no place does an individual exhibit himself more completely in his true colors than in a Boarding-House,” Seabury and Eliza must have found much to admire in one another, for love soon blossomed.
| … |
The Battery: The “Lover’s Lane” of Its Day
We can only imagine how Seabury’s courtship of Eliza played out. It must not have been easy, living under the same roof and the watchful eye of Mrs. Parker. No doubt the couple sought ways to escape the confines of the boarding house for some private moments. Most likely they walked to the Battery, a popular trysting place for lovers, where the paved walkway, the stately trees that lined the waterside, and the fresh air made it seem like an oasis from the congestion of their neighborhood. Perhaps Seabury and Eliza, from this vantage point, admired the handsome private homes that lined State Street, and talked about their future.
Another romantic spot for young couples in search of privacy was the genteel Vauxhall Garden, located between Bowery and Broadway on what is now Lafayette Street. Seabury and Eliza perhaps hired a hackney coach (for 25¢ per person), up to this bucolic garden, where they could enjoy ice cream, and music or theatrical performances. (See my post of January 2018, Vauxhall Garden: The Coney Island of Its Day).
A Wedding and a New Home
Seabury and Eliza were married on June 13, 1820, at St. George’s Episcopal Church on Chapel (now Beekman) Street. Seabury was 40 years old; his young bride was 23. (See post of June 2016, “Seabury Tredwell to Eliza Parker:” A New York City Wedding) After their wedding, Seabury, by that time a successful merchant and real estate investor, no doubt was eager to find a home for himself and his new bride; one that would provide the privacy he had long been without, and which would be large enough for a family. Most likely Seabury knew of the attractive house for sale on fashionable Dey Street through the advertisement that ran in the Evening Post from January 12 to February 3, 1820, which offered:
“The very neat two story house, No. 12 Dey street, brick front and iron railings. The house is replete with every convenience and is in excellent order.”
Seabury must have rented the house after his marriage, for the 1821 Directory lists his home address as 12 Dey Street. In the 1822 Directory, however, Seabury is listed at 34 Cedar Street, which was another boarding house, located east of Broadway near Pearl Street. It was surprising to discover that in May of 1822, an advertisement ran in the Evening Post, offering boarding to to “a few gentlemen” with “a small respectable private family” at 12 Dey Street. The ad asked that inquiries be directed to“Rev. M’Vickar, Columbia College” This no doubt was Reverend John McVickar (1787-1868), Professor of Moral Philosophy and Rhetoric at Columbia College. It is unclear why Seabury moved out, and Rev. McVickar moved in.
By 1823, Seabury and Eliza, along with their two-year-old daughter, Elizabeth, were back in the house on Dey Street. According to New York City Land Records, on April 1, 1823, Seabury purchased the house from Elizabeth Gillespie, widow of dry goods merchant George Gillespie, for $6,000. Seabury and Eliza made their home and raised their family at 12 Dey Street for 12 years, until 1835, when Seabury retired and bought the house on Fourth Street.
Moving Up in the World
Today, Dey Street today runs only two blocks, from Broadway to Church Street, but in Seabury’s day it was much longer, running all the way to West Street. Homes built on this street were brick rowhouses, typically 75-80 feet long by 25 feet wide, and therefore were large enough to accommodate a growing family. The house at 12 Dey, which was close to Broadway, had a new cistern and two grapevines in the garden. And Dey Street was on the fashionable, respectable west side of Broadway. Being the lady of the house on Dey Street was quite a social climb for Eliza, who spent her childhood in the poor Fourth Ward. In 1823, settled in their new home in the respectable, genteel part of town, Seabury and Eliza had arrived in elite society.
Sources:
- Albion, Robert Greenhalgh. The Rise of New York Port [1815-1860]. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1939.
- Bayles, William Harrison. Old Taverns of New York. New York: Frank Allaben Genealogical Company, 1915. www.gutenberg.org. Accessed 4/2/19.
- Burrows, Edwin G. And Mike Wallace. Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- City of New York. Minutes of the Common Council, May 1805. www.archive.org. Accessed 4/1/19.
- Costello, Augustine E. Our Firemen: A History of the New York Fire Departments, Volunteer and Paid. New York: Augustine E. Costello, 1887. www.archive.org. Accessed 3/15/19.
- Evening Post. July 12, 1805, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 4/1/19.
- Evening Post. May 13, 1812, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 4/2/19.
- Evening Post. January 12, 1820, p. 3. www.nespapers.com. Accessed 1/29/19.
- Evening Post. June 14, 1820, p. 2. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 7/23/15.
- Evening Post. May 22, 1822, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 4/3/19.
- Gamber, Wendy. The Boardinghouse in Nineteenth Century America. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
- Gunn, Thomas Butler. The Physiology of the New York Boarding-Houses. New York: Mason Brothers, 1857. www.archive.org. Accessed 3/26/19.
- Hardie, James. An Account of the Malignant Fever, Lately Prevalent in the City of New-York. New York: Hurtin and M’Farlane. 1799. U.S. National Library of Medicine. www.collections.nlm.nih.gov. Accessed 3/30/19.
- Landmarks Preservation Commission. Treadwell Farm Historic District, Borough of Manhattan. December 13, 1967, Calendar No. 3 LP-0536. www.s-media.nyc.gov.
- Longworth’s American Almanac, New-York Register, and City Directory. New York: David Longworth, 1796-1835. www.digitalcollections.nypl.org.
- McAtamney, Hugh Entwistle. Cradle Days of New York (1609-1825). New York: Drew & Lewis, 1909. www.books.google.com. Accessed 4/5/19.
- Moore, William H. History of St. George’s Church, Hempstead, Long Island, N.Y. New York: E.P. Dutton, 1881. www.archive.org. Accessed 2/8/19.
- Moss, Frank. The American Metropolis: from Knickerbocker Days to the Present Time. New York: P.F. Collier, 1897. www.archive.org. Accessed 4/4/19.
- New York Land Records. Conveyances 1823 vol. 164-167. www.familysearch.org. Accessed 3/30/19.
- Scherzer, Kenneth A. The Unbounded Community: Neighborhood Life and Social Structure in New York City, 1830-1875. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 1992.
Meet the Tredwells: The Ancestry of Seabury Tredwell
by Ann Haddad
With this post on the ancestry of Seabury Tredwell, we begin a new blog series: “Meet the Tredwells.”
A note about the variation of the spelling of Tredwell: Although early records seem to use “Tredwell” and “Treadwell” interchangeably, by the second generation in America “Tredwell” was used exclusively to denote this branch of the family. For the sake of clarity, this post will just use the spelling “Tredwell.”
In England
Seabury Tredwell’s ancestry can be traced as far back as 16th century England, to one Thomas Tredwell of Sibford Gower (before 1510-1545). His son, Alexander of Swalcliffe and Epwell (d.1603) was the father of Thomas (born c.1565). Thomas’ son Edward would leave England for the Colonies and begin the story of the Tredwell family in America.
Edward Tredwell, Emigrant
In 1635, Seabury Tredwell’s great-great-great-grandfather, Edward Tredwell (1607-1660), with his wife and two young children, emigrated from the small village of Swalcliffe, Oxfordshire, England, the seat of the prosperous Tredwell family. The family settled in the town of Ipswich, Massachusetts Bay Colony. In February 1637, the Massachusetts Bay Company granted Edward six acres of land “for planting.” Edward was one of over 20,000 emigrants who fled England for political, religious, and economic reasons, during what is known as the “Great Migration,” 1620-1640, and settled in New England.
And thus commences the story of the branch of the Tredwell family from which Seabury Tredwell (1780-1865) descended. The chronicles of this family, like the millions of others who came, and continue to come, to America, reflect the pursuit and attainment of the American Dream of peace, prosperity, and freedom.
In the ensuing years, Edward Tredwell, his wife, Sarah (nee Howes, 1609-1684), and their six children lived in the Colony of New Haven, and then Southold, on the North Fork of Long Island. By 1660, the year of his death, Edward Tredwell lived in Huntington, Long Island, then an agricultural area on the North Shore. No doubt he was a successful farmer, for upon his death his estate inventory was valued at 285 pounds sterling, a significant sum at that time.
John Tredwell, Esquire
Seabury’s great-great-grandfather, John Tredwell (c.1644-before 1720), son of Edward and Sarah, moved from Huntington to Hempstead, Long Island, sometime around 1662. By 1685, John was farming 350 acres of land in Hempstead, an area known for its fertile ground, and for its abundance of wild game and fish. Throughout his adult life, John held many notable positions in the town, including assessor, county justice, auditor, constable, overseer, and surveyor. In court and civil records he was always referred to as “Gentleman” or “Esquire.” He married twice, first in 1666 or 1667 to Elizabeth Starr (who died before 1682), then to Hannah Smith (born before 1706-death unknown). In 1696, John purchased a 250-acre farm from John Kissam of Madnan’s Neck (now known as Great Neck), North Hempstead. It was the homestead of the Tredwell family for the next 100 years.
John Tredwell had two children with his first wife, Elizabeth. It is unknown if he had any children with his second wife, Hannah.
Thomas Tredwell, Captain of the Militia
Seabury’s great-grandfather, Thomas Tredwell (before 1676-1722), son of John and his first wife, Elizabeth, continued farming the land at Madnan’s Neck; like his father, he also served as a vestryman and warden of St. George’s Church in Hempstead. In 1697, he was appointed by the Governor of the Province of New York to the office of Captain of a Company of Foot in Colonel Thomas Willet’s regiment. He held this position until his death, in 1722. His wife, Hannah Denton, whom he married sometime before 1698, died in 1748. Thomas and Hannah Tredwell had eight children. Clearly the Tredwell family had become wealthier over the years, for after his death Thomas Tredwell’s estate was valued at 825 pounds sterling.
Colonel Benjamin Tredwell
Seabury’s grandfather, Benjamin Tredwell (1702-1782), son of Thomas and Hannah, married his first wife, Phebe Platt, in 1727; she died in 1738 at the age of 28 years old. In 1739 or 1740, he married Sarah Allen (1717-1782). Benjamin, like his father and grandfather before him, was a farmer and a vestryman in St. George’s Church; he would later be instrumental in the building of a new church building in Hempstead.
He served as a Major in Colonel John Cornell’s regiment of the militia, and by 1750 was ranked as Colonel. According to Henry Onderdonk, Jr., in his Queens County in Olden Times (1865), Benjamin Tredwell was described as “a gentleman who ever supported an unblemished character and was remarkable for his hospitality, cheerfulness and affability.” Benjamin died just four months after the death of his second wife, Sarah.
Benjamin had four children with his first wife, Phebe, and five with his second wife, Sarah.
.
Doctor Benjamin Tredwell, Adventurer
Seabury’s father, Benjamin Tredwell, Jr., (1735-1830), son of Benjamin and his first wife, Phebe, lived a long and eventful life in Hempstead and later in East Williston, part of the town of Westbury. In 1756, as a 22-year-old physician and surgeon (likely trained by apprenticeship), he joined a privateering expedition against the French during the Seven Years War (1756-1763) on board the ship Hercules.
Marriage to a Mayflower Descendent
Six years after completing the voyage, Dr. Benjamin Tredwell married Elizabeth Seabury (1743-1818), daughter of Reverend Samuel Seabury (1706-1764), who was rector of St. George’s Church from 1742 to 1764; her half-brother, also named Reverend Samuel Seabury (1729-1796), became the first Episcopal Bishop of the United States (see “Uncle Sam(uel): Bishop, Loyalist … Broadway Star? from July, 2016). Elizabeth’s third great-grandfather was John Alden, who with his future wife, Priscilla Mullins, arrived in the New World aboard the Mayflower in 1620.
A Loyalist Brush with the British
During the Revolutionary War, in August 1776, British troops occupied Long Island and imposed martial law. Hempstead and its Churches of England were centers of military and Loyalist life. Dr. Tredwell, a vestryman of St. George’s, was an ardent Loyalist; in fact, he was one of the signers from Queens County of the Declaration of Loyalty to the King, dated October 21, 1776. At one point during the war, he quartered Hessian soldiers at his home; this show of loyalty to the King, however, did not prevent him and many other Loyalists from being denied favor and enduring mistreatment by the British. In 1776, while riding alone, he was robbed of his valuable horse by Lieutenant-Colonel Birch, Commander of the 17th Light Dragoons. The eminent physician was sent home carrying his saddle. When he protested the injustice of the theft, Dr. Tredwell was labeled a “rebel” and threatened with arrest.
A Rabble of Rebels
Dr. Benjamin Tredwell’s wife, Elizabeth, also beloved by the community and known for her hospitality, was involved in an what must have been a frightening incident during the Revolution: on August 2, 1780, while returning from New York City in a chaise, she was robbed of her horse and money by a group of militant patriots. Her eight-year-old son, Adam, who in his adulthood became a successful fur merchant in New York City, was with her at the time. It is extremely fortunate that Mrs. Tredwell was unharmed during this incident, for one month later, on September 25, she gave birth to the eighth of her nine children, Seabury Tredwell.
Slavery and Servitude
The presence of the institution of slavery on Long Island during the 17th and 18th century is clearly documented in the historical record. Slave records exist in Long Island as early as 1683. Four generations of Seabury’s ancestors owned slaves who worked the Tredwell farms. According to the 1800 Federal census, Benjamin Tredwell, Seabury’s father, owned six slaves. Slavery was finally abolished in New York in 1827.
Dr. Benjamin Tredwell also hired indentured servants to work for him; indentures were legal contracts that bound a person to work for another for a specified period of years. In 1826, Benjamin Tredwell paid for an advertisement in the Long-Island Star, in which he offered $5 for the return of one James Carman, a runaway. Servitude remained legal in New York State until its abolition in 1917.
Slaves Freed
With the creation of the New York Manumission Society in 1785, abolitionist New Yorkers set about promoting the gradual manumission (release from slavery) of slaves. New York passed its first gradual emancipation law in 1799. This law provided that all children born into slavery after July 4, 1799 in the state would be freed when they turned 25 (for women) or 28 (for men). This meant that slaveholders would be able to retain their slaves during their most productive years. Slavery was finally abolished in New York in 1827.
Dr. Benjamin Tredwell legally freed three of his slaves in 1808, 1810, and 1819, by signing manumission registration certificates. The three slaves were adults at the time they received their freedom. Dr. Tredwell, along with the Overseers of the Poor of Queens County, who issued the certificates, had to guarantee that each freed person was “of sufficient abilities to provide for himself.” He retained at least one slave, however; in his Last Will and Testament, dated September 21, 1829, he bequeathed his “female slave, Cloe,” to his son Benjamin. Although this was illegal, it most likely was by mutual consent. If Cloe was incapable of supporting herself (perhaps she was elderly or disabled), this could be viewed as at act of charity. If she did not live with Benjamin’s son, her only other option, most likely, was the almshouse.
“Esteem and Confidence”
Family lore has it that on the birth of each of his children, Dr. Tredwell planted an evergreen tree in front of his house. By 1784, with the birth of his last child, George, Benjamin would have planted nine evergreen trees. All of Benjamin and Elizabeth’s children lived to adulthood.
Upon his death at the age of 95, Dr. Benjamin Tredwell’s obituary in the Long Island Telegraph and General Advertiser (June 24, 1830), stated:
“Such is said to have been the esteem and confidence of the community in this aged Physician, that to the last, he retained a large portion of the practice in the neighborhood where he resided.”
The next blog post in the series “Meet the Tredwells” will explore the fascinating story of Eliza Earle Parker Tredwell’s ancestors.
.
.
.
Sources:
- Ancestry.com. 1790 and 1800 United States Federal Census. [database on-line]. Provo, UT, USA: ancestry.com Operations, Inc., 2010. Accessed 3/11/16.
- Ancestry.com. New York County, New York, Wills and Probate Records, 1658-1880 (NYSA) [database on-line]. Provo, UT, USA; ancestry.com Operations, Inc., 2015. Accessed 2/11/19.
- Ancestry.com. New York, Wills and Probate records, 1659-1999 [database on-line]. Provo, UT, USA: ancestry.com Operations, Inc., 2015. Accessed 2/11/19.
- Cutter, William Richard, ed. American Biography: A New Cyclopedia, Vol XL. New York: The American Historical Society, Inc., 1930, pgs. 177-178.
- Hawk, Alan J. “ArtiFacts: Benjamin Tredwell Jr.’s Amputation Knives.” Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research (2018) 476: pgs. 1715-1716. www.researchgate.net. Accessed 2/8/19.
- Hoff, Henry B. Genealogies of Long Island Families, Vol. II. From The New York Genealogical and Biographical Record. Volume II. Baltimore, Maryland: Genealogical Publishing Co., Inc, 1987.
- Jones, Thomas. History of New York During the Revolutionary War, Volume I. New York: The New York Historical Society, 1879, p. 114-116. www.internetarchive.org. Retrieved 3/12/16.
- Long-Island Star (Brooklyn, New York) 23 November, 1826, Thursday, p. 3. www.newspapers.com. Accessed 3/11/16.
- Luke, Dr. Myron H. Vignettes of Hempstead Town 1643-1800. Hempstead, New York: Long Island Studies Institute, 1993.
- Mather, Frederic Gregory. The Refugees of 1776 from Long Island to Connecticut. Albany, N.Y.: J.B. Lyon Co., 1913, p. 607-608. www.internetarchive.org. Retrieved 5/5/16.
- Moore, William H. History of St. George’s Church, Hempstead, Long Island, N.Y. New York: E.P. Dutton, 1881. www.archive.org. Accessed 2/8/19.
- Onderdonk, Jr., Henry. Documents and Letters Intended to Illustrate the Revolutionary Incidents of Queens County. New York: Levitt, Trow and Company, 1846., p. 117-128, p. 172-173, p. 244-249. www.ancestry.com. Accessed 3/11/16.
- Robbins, William A. “Descendants of Edward Tre[a]dwell Through His Son John.” The New York Genealogical & Biographical Record. April, 1912 (Volume 43, No. 2), p. 127; Ibid., July, 1912, (Volume 43, No. 3), p. 221; Ibid., Oct, 1912 (Volume 43, No. 4). www.archive.org. Accessed 2/8/19.
- Smith, Dean Crawford. The Ancestry of Eva Belle Kempton, 1878-1908, Part II: The Ancestry of Amanda Spiller 1823-1873. Boston: New England Historic Genealogical Society, 2008.
- St. George’s Episcopal Church Archives. New York, NY. Record of St. George’s Church/Baptisms 1809-1830/Marriages 1816-1837.
- Treadwell, Thomas Alanson. “Tredwells in Search of Tredwells: Adventures in Ancestry.” New York Genealogical and Biographical Record, 104, No. 4 (1973): 195-204.
- Tredwell, Thomas Allison., “Tredwells in Search of Tredwells” in New York Genealogical and Biographical Record, 104 (1973): 195-204.
- Wilson, James Grant, ed. The Memorial History of the City of New York: From Its First Settlement to the Year 1892 Volume II. New York: New-York History Company, 1892. www.archive.org. Accessed 2/11/19.